Robotic Assisted Total Hip Replacement
Robotic Assisted Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement is an excellent solution for patients suffering from end stage hip arthritis. Conventional total hip replacement surgery carries a high success rate although complications can occur. Complications including dislocation, leg length discrepancy and wear of the artificial prosthesis are related to how well the surgery was executed and the alignment of components.
In the past decade, biomaterial advancement for joint replacement surgery has reached its plateau with highly crossed linked polyethylene prolonging the longevity of total hip replacement. Research and development have been shifted toward improving surgical precision and execution. Navigation can provide real time data on implant placement and leg length intraoperatively, but execution is still uncontrolled and at risk of error.
Robotic assisted total hip replacement has emerged in recent few years. Preoperatively, patients undergo CT scans which enables a three-dimensional assessment of their anatomy. Accurate sizing and positioning of both the acetabular and femoral components can be planned. Leg length and offset adjustment can be quantified. During surgery a tracker is placed over the pelvis and registration of patient’s landmarks is completed to match with preoperative CT images. Bone removal over the acetabular side is subsequently performed under haptic control by robotic arm. The robotic arm will only active while the surgeon operates within the preplanned boundaries, once the instrument moves outside of the boundary, the robot shuts down. The end result is a more precise and safer bone removal with lower risk of injuring surrounding structures. Implantation of the acetabular component is also controlled by the robotic arm which precisely controls the direction of cup impaction. Femoral preparation is done manually but the robotic system provides real time feedback for adjustment of leg length and offset.
International studies have shown promising early results. Several studies have shown significant increase in accuracy of implant positioning and correlation with preoperative planning, resulting in lower short-term complication rates (eg dislocation). Most studies report higher patient satisfaction rate. When managing patients with complex deformities for example hip dysplasia, ankylosing spondylitis with fusion, prior acetabular fracture with hardware, robotic technique provides added advantage of enhancing planning and precise execution, significantly simplifying these difficult surgeries.
Drawbacks of robotic surgery include cost, longer operation time and tracker pin related complications. Long term data is still lacking for revision rates and patient reported outcome, but with increasing utilization, these results will soon be available.
Patients now have more treatment options they can choose from.
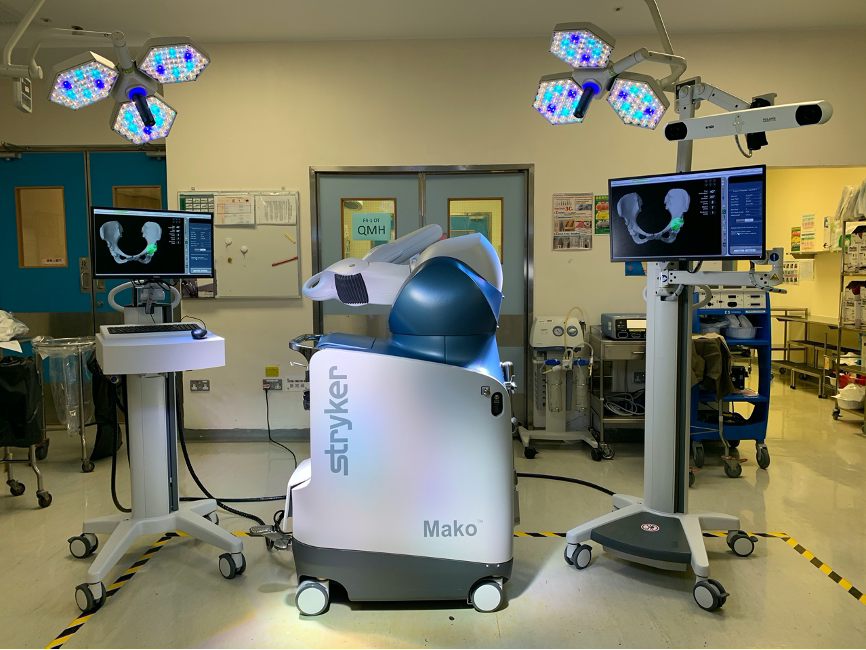
Image 1) Robotic arm assisted joint replacement surgical system
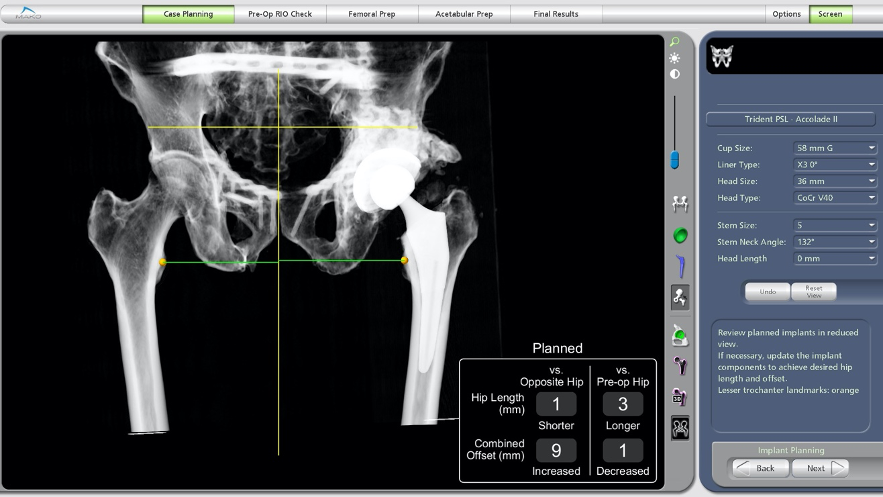
Image 2) Patient with previous acetabular fracture planning for robotic assisted total hip replacement
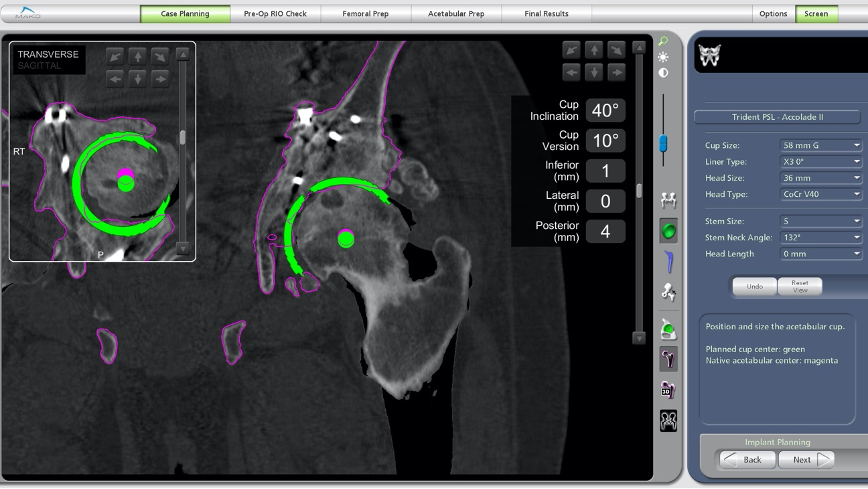
Image 3) Using three dimensional CT scans for planning, previously inserted plates and screws can be avoided
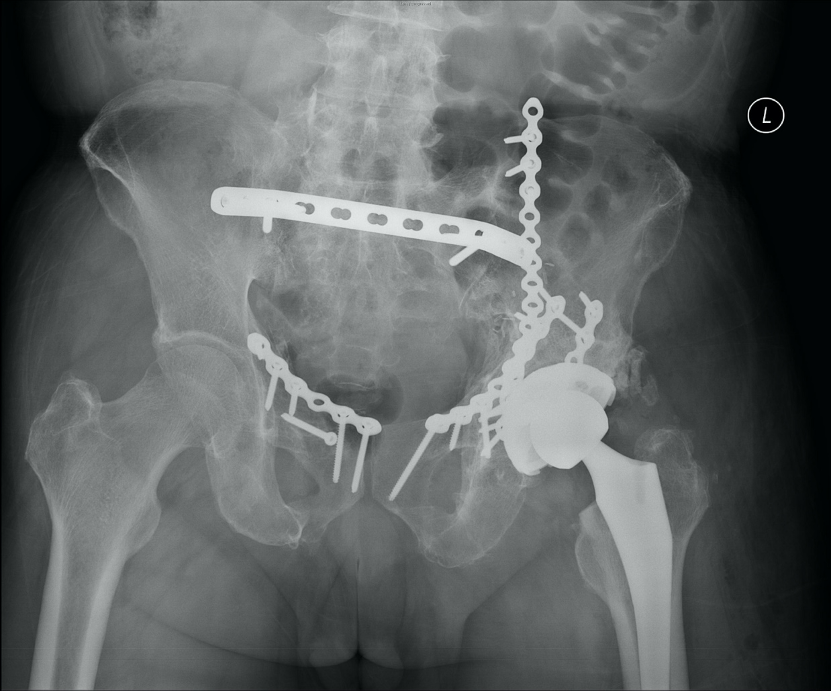
Image 4) Patient underwent robotic assisted total hip replacement surgery, previously inserted screws and plates were left in place, simplifying the surgery
Dr. Henry Fu