Introduction
Anatomy
Cause
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Non-surgical treatment
Surgical treatment
Rehabilitation
Prevention
Introduction
Bacteria infection and gangrene in the foot are common problems faced by diabetic patients. In severe cases, the affected lower limb may be amputated.
Anatomy
Since the feet are organs located the farthest away from the heart, a wound in the feet could lead to infection due to the lack of blood supply – a condition commonly found among chronic diabetes patients.
Cause
There are two reasons for diabetic foot: complications of the nervous system and blocked blood circulation. Complications of the nervous system could rob the foot of its normal sensations, render the toes deformed and the skin dry, making the toes prone to injury. Blocked blood circulation in the foot is due to the degeneration of blood vessels’ structure as a result of diabetes. Because of the lack of blood circulation, it would be difficult for any wound in the foot to heal after an injury. This could then easily lead to bacteria infection.
Symptoms
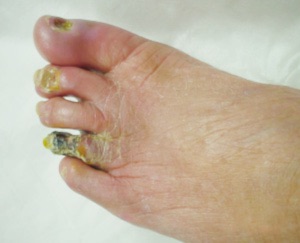
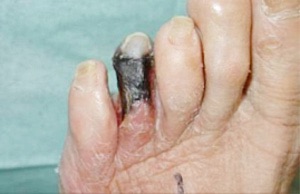
The most common symptom is numbness in the foot. Other symptoms include ulcer, bacteria infection and even gangrene.
These symptoms usually develop very slowly so that in the beginning, the patient is usually not aware of them except that the skin of the foot – in particular, the toes – starts to feel less or more sensitive. Gradually, there is a sense of numbness and pain. The type of pain varies among different patients. It could be sharp pain, burning sensation, biting pain or scorching pain. Sometimes the patient may feel as if ants are crawling on the skin. Because of the lack of normal sensations, the patient could easily get injured without knowing it.
Diagnosis
If you are a diabetic patient, you should perform self-diagnosis on a regular basis. Check if there are any injuries to the toes and toe nails. Use a mirror to help you check the soles of your feet. If you have weak eyesight, ask your family or friends to help you do the checking. If you discover any wounds, redness, swelling, heat, pain or discharge on your foot, visit your doctor immediately.
Non-surgical treatment
The most important medical treatment is to control the blood sugar level. Antibiotics are prescribed for controlling infection, such as cellulitis. Superficial ulcers usually can be treated by dressing the wound. Deeper and chronic ulcers will not heal and surgical treatment may be required.
Surgical treatment
It is relatively difficult to treat obstructed blood circulation in the foot region. Unhealed chronic ulcers with or without infection usually require surgery to remove the dead and infected tissue to control the infection and coverage of the skin defect. Sometimes amputation is unavoidable if the infection cannot be controlled.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is important because people with chronic diabetes are more likely to have poor blood circulation. The first and best advice is to check the skin and toenails of the feet every day. Many people with diabetes also have lost the normal sensation in their feet. They don't feel small sores or changes in the skin. Wearing white socks can also help the patient detect any oozing or bleeding from the sores or wounds.
Prevention
Proper foot hygiene and care helps reduce the chances of ulcer and bacteria infection. It is, however, relatively difficult to prevent the blockage of blood circulation. But proper foot care can delay the need for amputation.
Here are some tips for proper foot care:
Clean the feet every day.
If the skin of the feet is dry, use a small amount of lotion to moisten it.
Keep the sky between the toes as dry as possible.
Choose comfortable shoes. There should be enough room in the shoe box and the shoe should be made with soft material that allows proper ventilation.
Wear socks that are made with cotton or wool. Do not wear socks made with man-made fibres or socks with patterns, as these provide poor ventilation and could create friction on the feet, making them prone to injury.
If the weather is cold, wearing socks to bed can help improve the feet’s blood circulation.
Do not wash the feet with water that is too hot. Test the water temperature with your fingers or with a thermometer before putting your feet in the water.
Visit the family doctor for regular check-ups of the feet.
Cut your toe nails regularly. The edge of the toe nails should be flat and straight.
Do not cut callus or corns with scissors.
To avoid injury, do not walk bare-footed.
Check the shoes to see if they contain any sharp or hard objects to prevent injuries.
Dr. NGAI, Wai-kit