Anatomy
Pelvic fractures
Treatments
Surgical treatments
Complications
Anatomy
The bony pelvis consists of the sacrum, coccyx and the left & right hemipelvis (including ilium, ischium and pubis). It is a hard structure that protects the viscera (i.e. bladder, large bowel, vagina, uterus and ovaries), connects the spine to the lower limbs and transfers body weight. It is the strong ligaments and tension of the pelvic floor that account for pelvic stability and the inner wall of the pelvic girdle is full of blood vessels and nerves. As such, serious pelvic fracture can produce significant internal bleeding and nerve damage.
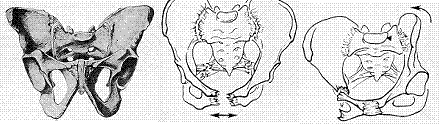
Pelvic fractures
High-impact traumas, such as road traffic accidents or falls from significant height, can result in pelvic fracture. These traumas are usually associated with severe blood loss, which is not as easily detected as in other limb fractures. For most of the limb fractures, orthopaedic surgeons can assess the amount of blood loss by the degree of swelling and bleeding of the fractured area; in most of the pelvic fracture cases, lost blood will stay in the damaged girdle, and it is difficult to diagnose extensive blood loss by inspection of the damaged region alone. The patient’s condition can deteriorate quickly, leading to shock or even death. Other possible traumas associated with the fracture include: rupture of bladder and urethra, tear of large intestine, rupture of vagina (women), acetabulum fracture or hip dislocation, femur fracture, patella (knee cap) fracture, traumas on knee joint (e.g. rupture of posterior cruciate ligament) and ankle or foot fractures.
Treatments
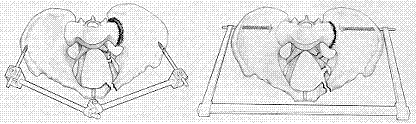
Orthopaedic surgeons will perform thorough physical examination to see if there are traumas in other parts of the body (skull, chest, abdomen and spine). Cleaning is required for any wounds and antibiotics will be prescribed to prevent infection. Further investigations will further include X-ray and Computed Tomography Scan(CT). If severe internal bleeding is suspected or shock has occurred, it is essential to rule out other possibilities; such as internal bleeding in the chest and abdomen. Should pelvic fracture be the main cause of internal bleeding, orthopaedic surgeons will apply an external fixator to reduce and immobilize the fracture site. Blood transfusion will be given in advance to stablise the blood pressure. If instability of blood pressure and shock persists, arterial embolization can be used to stop bleeding; under critical condition, orthopaedic surgeons will consider open surgery for bleeding control. Death rate due to pelvic fracture can be as high as 50%.
If there are no wounds or shock and there is only hip joint dislocation, reduction should be commenced immediately to ease pain and prevent sciatic nerve being compressed. Sometimes metal pin will be inserted to the tibia for temporary traction. Orthopaedic surgeons will prescribe painkillers and assess the fracture condition before surgery using X-ray and CT scan. If the fracture or hip joint is minimally displaced, non-surgical treatment is adopted. Patients need to stay in bed for one to two weeks and should impose no stress on the affected limb for three months, by using a crutch to help walking. If displacement of the fractured pelvis is not properly treated, leg length inequality and chronic hip & back pain might occur. Surgical treatment is the common option here, which will usually be performed within five days of injury. Rehabilitation process is similar after conservative and operative treatment.
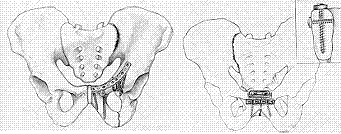
Surgical treatments
Bone plates and screws are the most common surgical devices. The surgery starts with reduction of the fracture site, using bone plates and screws to stabilise the affected bone; in comminuted fracture, bone graft procedure is needed. Casting is usually not necessary after surgery and patients can start physiotherapy in two to three days. A special motion machine will be used to facilitate mobilization of lower limbs in bed. The affected limb should be kept not weight bearing for 12 weeks and a crutch will be used to help walking. Unless otherwise required, bone plates and screws do not need removal. There are two common surgical approaches; i.e. anterior and posterior access, each has its advantages and risks. In certain type of pelvic fracture cases, application of minimally invasive surgery under computer assisted navigation can minimize trauma to patients.
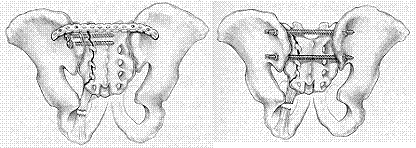
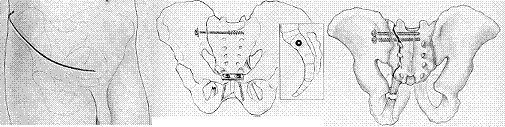
Complications
1. General
Complications related to anesthesia (the surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia)
Wound infection
Bleeding or hematoma formation
Improper wound healing
Deterioration of pre-existing illnesses, such as high blood pressure, stroke or diabetes
2. Specific to the surgery
Bone screws, pins or plates loosened or impingement
Non-union (poor fracture healing)
Malunion (fracture heals in unsatisfactory alignment; the deformed pelvis may make normal delivery difficult)
Affect hip joint function
Friction and pain caused by internal fixation devices
Numbness due to damage of nerves
Risk of leg length inequality (in complicated comminuted fracture cases)
Complications related to anterior surgical approach
Inguinal hernia
Damage of nerves of anterior thigh
Damage of femoral arteries / veins (ruptured or blocked) / lymphs at the groin
Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Damage of vas deferens (men)
Complications related to posterior surgical approach
Damage of sciatic nerve
Stiffness of joint owing to scarring or excess new bone in the soft tissue
Avascular necrosis of femoral head
Dr. NGAI Wai-kit